Rehabilitation Program: Executive Functions
Click to try FREE for 15-Days.
This module is specifically designed to train executive functions, including reasoning (capacity to make deductions from hypotheses) and strategy. It contains language-based tasks and visual activities.
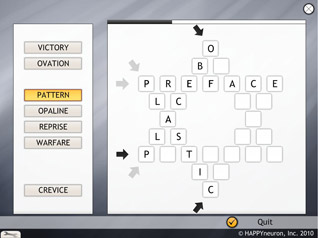
Writing in the Stars
The task
Heavenly inspiration is required for this new twist on the old cross-word puzzle. The user is given a list of nine words. Only six of them can be used to fill the empty squares and connect with each other to form the six-point star.
What it trains
Making travel plans, keeping track of various appointments, engaging in group dynamics at work or at a social event, to evaluate a colleague's ideas and then to reflect on the work are all examples of executive functioning. Indeed, this exercise aims at training the patient's capacity for logical reasoning. In order to determine which 6 words to choose from the list of nine, he has to try a number of logical combinations to find which positions of letters are common to two or three words.
Parameters
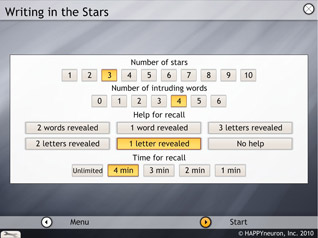
The parameters that can be selected are the number of stars (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, or 10), the number of intruding words (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6), the help for recall (2 or 1word revealed, 3, 2, or 1 letter revealed, or no help), and the time to recall (unlimited, 4, 3, 2, or 1 minute). The words are always seven-letter words.
Number of Unique Configurations
2,100 unique game configurations and significant data set depth.


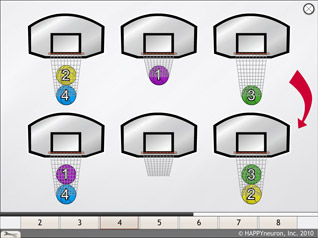

Basketball in New York
The task
This exercise sounds easy enough but it is deceptively challenging! The patient will see a first line of three hoops with colored basketballs inside. In the second line, he will have to mentally determine the number of basketball moves required to reach the same configuration (same color in the same hoop) as the first line of hoops.
What it trains
This is a problem-solving type of exercise. The user needs to mentally plan his action, strategize his next move, go back on the wrong moves and build his own reasoning in a concentrated way. This exercise trains also his visual mental imagery as he can't move the basketballs with the mouse. All the possible actions must be visualized in his mind.
Parameters
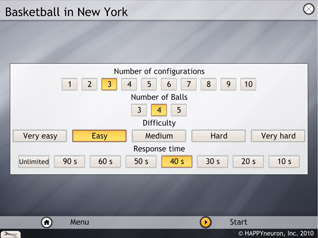
The parameters that can be selected are the number of configurations (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, or 10), the levels of difficulty (very easy, easy, medium, hard, or very hard), and the response time (unlimited, 90, 60, 50, 40, 30, 20, or 10 seconds). Five different colored basketballs are shown for each trial.
Number of Unique Configurations
1,200 unique game configurations and significant data set depth.


Decipher
The task
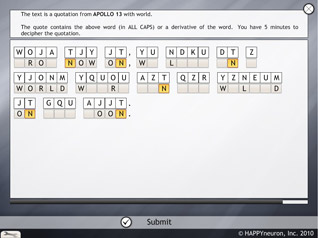
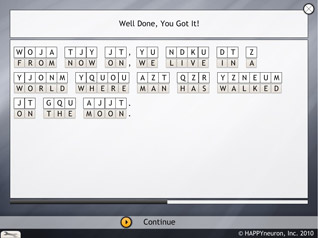
In this task, the patient is asked to decipher some famous quotations where the letters have been replaced, either by other letters or by symbols. To make the exercise easier, each letter is always replaced by the same letter or symbol. Cracking these secret codes is perfect practice if a person likes mysteries!
What it trains
This deciphering exercise trains the user's concentration and his capacity to deduce what is not directly written by linking the various pieces of information he is given and his own knowledge of language (spelling, grammar rules, and letter frequency). This will help him build a coherent quotation. This task also requires the collaboration of various cognitive skills: concentration, language (spelling, grammar rules, letter frequency), logic, and the capacity to make deductions from hypotheses.
Parameters
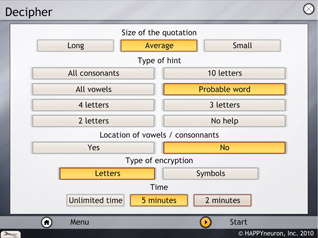
The parameters that can be selected are the length of the quotation (long, average, or small), the type of hint (all consonants, 10 most common letters, all vowels, probable word, 4, 3, or 2 letters from the quotation, or no help), the coloration of vowels/consonants, the type of encryption (letters or symbols), and the recall time (unlimited, 5, or 2 minutes). The display of rules is not available.
Number of Unique Configurations
Over 280 unique game configurations and significant data set depth.


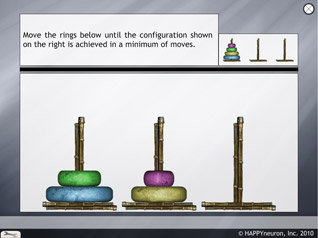


The Towers of Hanoi
The task
In this exercise, the patient must configure colored rings on a series of pegs in order to match a target. There are some rules to respect: He can move the top-most ring on each peg to another peg, but he can only move one ring at a time and he can never put a larger ring on top of a smaller ring. From time to time, a given peg may not hold any rings: he may move any available ring on to an empty peg.
What it trains
It is widely acknowledged in neuroscience and psychology research that problem-solving abilities rely not only on language-analytical reasoning but also temporal-spatial design skills that we use to visualize some problems.
Parameters
The parameters that can be selected are the number of moves (less than 5, 5 to 9, 10 to 14, 15 to 19, 20 to 24, 25 to 29, or more to 29), the number of rings (2, 3, 4, or 5), the number of tries (1, 2, or 3), the number of configuration (1, 2, or 3), and the allowed time (unlimited, 3, 2, or 1 minute).
Number of Unique Configurations
Over 460 unique game configurations and significant data set depth.


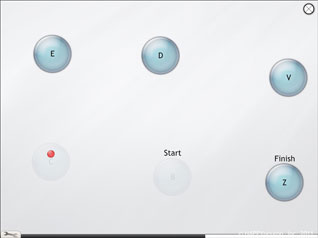
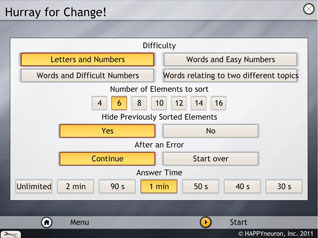
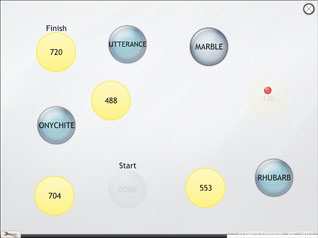
Hurray for Change!
The task
There are two tasks to this exercise. In the first part, series of 4 to 16 letters or words must be linked in alphabetical order. The second part demands to alternately sort two series of items.
What it trains
In addition to mental flexibility and strategy skills, this exercise requires concentration and visual and spatial exploration skills. Visual and verbal working memory skills are also stimulated, as well as language skills which are necessary when letters or words are involved. This game develops cognitive flexibility, that is, the ability to engage in one activity, disengaging andthen re- engaging. In real life, such a situation can occur when being engrossed in paperwork, suddenly the phone rins and must be answered, after which the person has to get back to their original task. The skills called upon in this game are constantly used in our daily lives. Another example is scanning for a name on a list or scanning a monitor for airline flight departures or arrivals screen. Further, in everyday life, one may use executive functions when reorganizing files or preparing the house for the holidays by simultaneously cooking various dishes when everything has to be ready at a different time!
Parameters
The parameters which can be selected are the type of the task (letters and numbers, words and easy numbers, words and difficult numbers, words related to 2 different topics), the number of elements to sort (from 4 to 16), the way previously sorted elements are handled (hidden or not), the behavior after a mistake (start over or continue) and the allowed answer time (from 30 seconds to unlimited).
Number of Unique Configurations
Over 780 unique game configurations and significant data set depth.


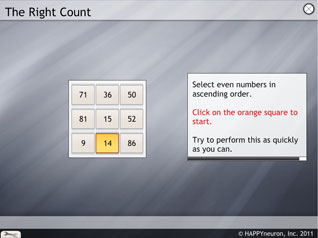
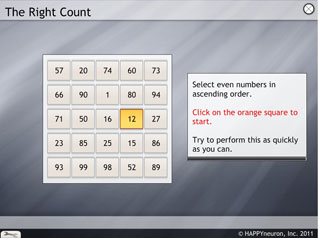
The Right Count
The task
In this exercise, the patient is asked to identify and sort out even and odd numbers in ascending or descending order.
What it trains
This exercise mainly involves executive functioning skills. It also requires both visual scanning, spatial exploration of the grid and a high degree of concentration. Memory also plays a role here as we utilize mental strategies that involve the storage and retrieval of information when recalling the location on the grid of numbers scanned earlier. Finally, you will also use your numerical processing skills as you order the numbers in ascending or descending sequence.
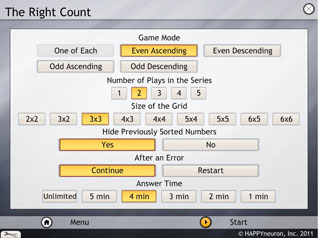
Parameters
The parameters that can be selected are the play mode (even ascending, even descending, odd ascending, odd descending or one of each), the number of series (from 1 to 5), the size of the grid (2x2, 3x2, 3x3, 4x3, 4x4, 5x4, 5x5, 6x5, or 6x6), the answer time (Unlimited, 5 minutes, 4 minutes, 3 minutes, 2 minutes or 1 minute). Other options can also be enabled: hide previously sorted numbers (yes or no), restart or continue after an error.
Number of Unique Configurations
Over 4500 unique game configurations and significant data set depth.



Ready, Steady, Count!
The task
How good is your mental arithmetic? Can you quickly tell if you have received the correct change at the store? In this game, you are asked to carry out mental calculations. In this exercise you are presented with a series of numbers and mathematical symbols to be used to perform some mental arithmetic calculations.
What it trains
This game trains working memory, executive function (calculation and arithmetic reasoning), mental imagery and your concentration. Concentration is an essential baseline skill that helps you to understand the objective of the game and read the numbers and symbols. Your working memory is essential to temporarily keep small amounts of information in mind while you perform the next cognitive step on that information. Finally, your executive functions are used to perform the arithmetic calculations.
Parameters
You can modify the number of series (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 15 or 20), the number of operations (from 1 to 3), the difficulty of numbers (from 1 to 9, from 10 to 20 or from 20 to 100), order of appearence (operators then numbers or numbers then operators), memorization time (unlimited or from 4 to 10 seconds per item) and restitution time (inlimited or 120, 60, 50, 40, 30, 20 or 10 seconds).
Number of Unique Configurations
Over 9000 unique game configurations and significant data set depth.
Click to try FREE for 15-Days.
